Huzhou University and Army Medical University Collaborate to Develop Bionic Nanogel for Rapid Hemostasis
In a significant medical breakthrough, researchers from Huzhou University and Army Medical University have joined forces to develop a bionic nanogel that can achieve rapid hemostasis within just 5 seconds. This innovative technology, activated by blue - light laser, shows great promise for patients suffering from gastrointestinal bleeding, especially those with coagulation disorders.
Gastrointestinal bleeding is a common and life - threatening clinical condition. Existing treatments, such as the use of thrombin, often face limitations in the unique environment of the digestive tract, particularly when dealing with patients having chronic liver diseases or impaired blood - clotting abilities. The new bionic nanogel aims to revolutionize the treatment of such cases.
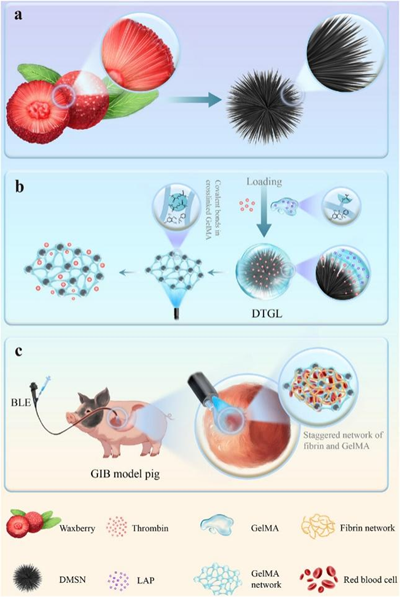
The research team drew inspiration from the micro - fiber structure of bayberry fruit. They successfully created a nano - silica carrier with a bayberry - like structure, which is then coated with methacrylated gelatin. When activated by blue - light laser under endoscopic guidance, this system forms a stable and intelligent nanogel network.
The unique micro - fiber structure of the bayberry - inspired nanogel is key to its effectiveness. The nanogel's design allows for a large surface area, enabling it to interact with the bleeding site more efficiently. The methacrylated gelatin coating not only provides excellent adhesion properties but also plays a crucial role in the gel - forming process upon blue - light activation.
Clinical trials have demonstrated the remarkable efficacy of this new nanogel. In simulated gastrointestinal bleeding scenarios, the nanogel was able to initiate the blood - clotting process within 5 seconds. This rapid response can be a game - changer in emergency situations where every second counts.
For patients with coagulation disorders, the nanogel's performance is particularly encouraging. Traditional hemostatic methods often struggle to achieve satisfactory results in these patients. However, the bionic nanogel's ability to quickly form a stable clot regardless of the patient's underlying coagulation problems offers new hope for better treatment outcomes.
The bionic nanogel also exhibits outstanding stability and adhesion. Once applied to the bleeding site, it firmly attaches to the tissue, preventing further blood loss. The stable gel network formed after blue - light activation can withstand the mechanical forces within the gastrointestinal tract, ensuring that the clot remains in place during the crucial initial stages of wound healing.
This high - level adhesion is due to the specific chemical and physical properties of the nanogel's components. The methacrylated gelatin has functional groups that can interact with the tissue surface, creating strong bonds. At the same time, the nano - silica carrier provides a stable framework for the gel, enhancing its overall stability.
Although the research is still in its early stages, the potential of this bionic nanogel is immense. The research team plans to conduct more extensive clinical trials to further validate its safety and efficacy. In the future, they also aim to optimize the manufacturing process to make the nanogel more cost - effective and widely available.
This development could not only improve the treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding but also open up new possibilities for other applications in the medical field, such as wound healing in other parts of the body or in surgeries where precise and rapid hemostasis is required.